Our master student Yudong Liu proposed a study about Robot-Assisted Haptic Rendering of Bilateral Physical Tasks via Physical Engine in IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics.
Neurological injuries headed by hemiplegia are often the leading cause resulting in coordination decay. Bimanual robotic systems have demonstrated promising efficacy in recovering coordination of bilateral limbs. The main principle that bimanual robots work for physical therapy is through delivering motor tasks to resemble activities of daily life (ADLs). Current evidence also indicates that bimanual training outcomes can be improved by integrating the senses of haptics. However, majority of robotic systems have not been developed with the integration of haptic feedbacks, especially when required to meet the workspace of ADLs. This study sought to address this issue by developing a new haptic-integrated robotic system capable of delivering bilateral tasks. The system is implemented with robotic motion control and a physical engine integrated in Unity3d. Human users are expected to be able to perform bimanual trainings through interacting with dual robotic handles. Experiments were conducted to examine position tracing performance of motion control and haptic transparency of bimanual tasks rendered by the robot. The experimental results led us to believe that the developed robotic system can deliver bilateral physical tasks with haptics integration in an ADL-required workspace. Future work will examine its haptic performance in terms of real force feedback.
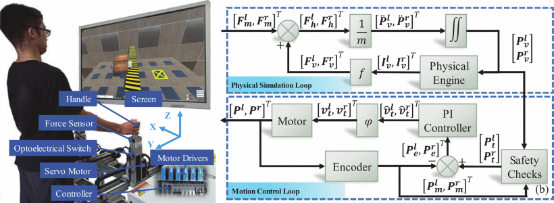
Yudong Liu is the first author of this article. Mingming Zhang, assistant professor at Southern University of Science and Technology, is the corresponding author of this article.
